裂褶菌 (Schizophyllum commune),又称白参菌,是我国传统的珍稀食药用菌,其富含多糖等多种生物活性物质。据古籍记载,裂褶菌常用于治疗小儿盗汗、妇科疾病及神经衰弱等。早在1986年,日本就批准了裂褶菌多糖(Schizophillan, SPG)注射液作为胃癌、胰腺癌和直肠癌的治疗药物。目前,工业上主要利用液态发酵法生产裂褶菌多糖。近几年,裂褶菌人工栽培逐渐兴起,在云南、贵州、湖北等地均有规模化生产,从子实体中获取多糖变得容易。湖北省农科院食用菌加工团队自2024年以来承担了国家重点研发计划课题“珍稀食用菌活性物质高值化利用及功能型产品开发(2024YFD2100802)”,项目组在裂褶菌子实体多糖提取利用及抗肥胖功能机制研究方面取得了系列进展。

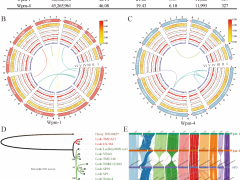
在国际学术期刊《Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture》(IF=3.5)上发表了题为“Physicochemical, antioxidant, gastrointestinal digestion and probiotic growth promoting properties of water and alkali extracted polysaccharides from Schizophyllum commune”的研究论文,揭示了水提和碱提裂褶菌子实体多糖体外消化规律及其促益生菌增殖作用。

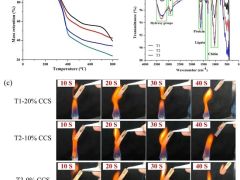
以“Effects of different drying methods on the physicochemical properties, antioxidant activity and gut microbiota fermentation behaviours of polysaccharides from Schizophyllum commune”为题在国际学术期刊《Food Research International》(中科院一区,IF=8.0)上发表论文,明确了不同干燥方式对裂褶菌多糖生物活性的影响。

在权威学术期刊《Food Chemistry》(中科院一区,IF=9.8)上发表了题为“Comparison of physicochemical properties of water- and alkaline-extracted polysaccharides from Schizophyllum commune and their anti-obesogenic effects in vivo”的研究论文,首次报道了裂褶菌子实体多糖在动物体内良好的抗肥胖及调节肠道菌群作用。
对裂褶菌多糖抗肥胖功能机制进行了深入解析,相关成果以“Schizophyllum commune polysaccharide ameliorates diet-induced obesity by regulating the Faecalibaculum rodentium/indole-3-lactic acid/microRNA axis”为题发表在学术期刊Carbohydrate Polymers(中科院一区,IF=12.5)上,明确了裂褶菌多糖通过啮齿粪杆菌/吲哚-3-乳酸/microRNA途径减轻饮食诱导的肥胖的作用机理。
上述研究明确了裂褶菌子实体多糖减肥降脂的健康效应及高效提取利用方法,结合项目组前期在食用菌多糖提取制备方面获得的相关专利技术,下一步将重点推进裂褶菌子实体多糖安全性评价研究以及减肥降脂功能性产品的开发。